The History of Arab Immigration to the United States

By: Adam Abdel-Qader / Arab America Contributing Writer
The History of Arab immigration to the United States dates back to before it gained its independence in 1776. Throughout all the waves of Arab immigration starting in the late 19th century, many motivations for migrating have existed. Some sought economic opportunities, some wanted to establish and hone their professions, and some migrated amid political unrest. Despite facing discrimination and prejudice early on in the United States, Arab Americans have made substantial contributions to American society through science, engineering, medicine, politics, law, and the arts.
Within the history of Arab immigration, there lies an opportunity to celebrate the rich and diverse contributions of Arab Americans to the fabric of American society.
Waves of Immigration:
First Wave:
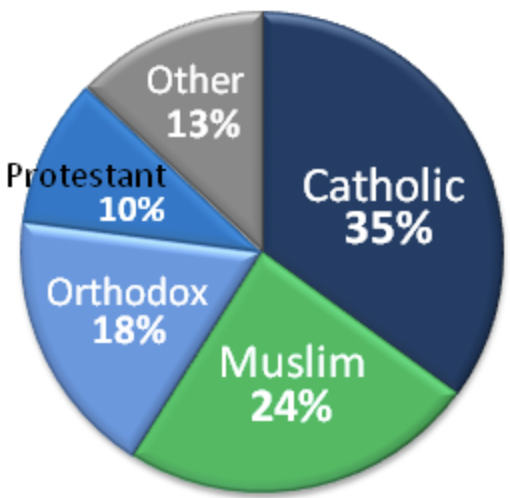
The first wave of immigration occurred late in the 19th century and lasted until the early 1920s. Most immigrants came from Lebanon and Syria and primarily consisted of Christian Arabs.
Some scholars account for this first wave as a search for adventure and rapid economic gain within the classic American dream. Other scholars assert that there was a combination of economic, religious, and political explanations for the migration.
While the literature differs on the reasons for the first wave of migration, one thing the research most definitely asserts is the notion that Arab immigrants at the time came without the idea of making it their permanent home. They were determined to create a living and share their wealth with their families back home. Eventually, they saw the long-term advantages of living in the United States. Subsequently, they settled in cities like New York, Boston, and Detroit. They established communities and created businesses from low-skilled labor industries such as textiles, clothing, and food processing.
Second Wave:
The second wave of immigration to the United States occurred in the mid-20th century. This wave primarily comprised Arabs from different nations such as Egypt, Syria, Iraq, Jordan, and Palestine.
The Arabs in this wave were mainly Muslims. They primarily came to the United States to pursue higher education, find valuable work that fit their expertise, and escape political turmoil. Many of these immigrants in this wave docked as educated professionals in science, engineering, education, medicine, politics, and law and therefore pursued skilled professions.
Most immigrants settled in urban areas and established larger communities than the previous wave. Eventually, these communities provided widespread support and resources for new incoming Arab immigrants.
Third Wave:
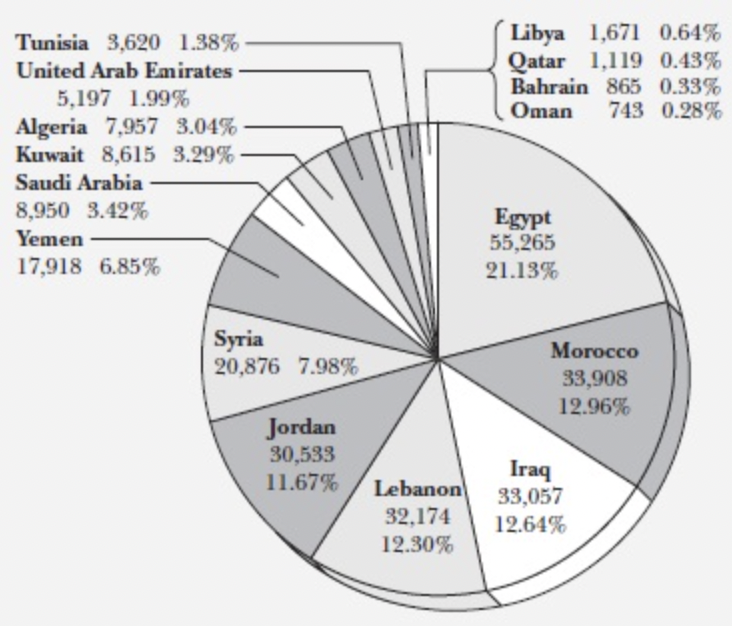
Although often split into two waves, the third and subsequent fourth wave, it is more manageable to generalize the 1970s to the present as the third wave of Arab immigration to the United States. This wave comprises immigrants from Arab nations such as Morocco, Iraq, Syria, Tunisia, Algeria, Yemen, Egypt, and Jordan.
The immigrants in this wave were primarily Muslim and came to the United States in light of finding political asylum, getting a better education, and finding valuable work. Many Arab immigrants in this wave were and are still incoming refugees, fleeing political unrest and turmoil in their home states.
Challenges Faced by Arab Immigrants:
Arab immigrants have faced many challenges in their journeys to the United States. However, once settled in the United States, they faced problems on the domestic front. They were often seen as exotic and foreign, and Muslim Arabs were often viewed with suspicion due to their religion. They also faced economic challenges and mainly worked low-paying jobs with poor working conditions.
The second wave of immigration faced similar challenges as they were often discriminated against because of their religion and ethnicity. They also faced economic challenges as they struggled to find jobs that matched their skill and education levels. As the more educated wave of immigrants, this notion was very detrimental. Many Arab immigrants in this wave faced political struggles as the United States government was frequently involved in political disputes and conflicts with Arab nations. Subsequently, there was increased scrutiny and suspicion of Arabs in general.
The third wave of immigration faced and still faces new challenges. Many Arabs were refugees and had difficulty adapting quickly to a new culture and language. The quick transition from one nation to another without preparation often made finding jobs and establishing themselves in new communities challenging. This notion was never previously a substantial issue in other waves.

Societal Contributions to the United States:
Arab Americans have made significant contributions to American society in various fields, including business, science, engineering, education, medicine, politics, law, and the arts; the list could go on.
Arab American businesses within the United States have been a continuing factor in the growth of the American economy by creating and generating profound revenue. Many Arab American entrepreneurs have started successful businesses and companies in many industries, including technology, healthcare, and finance.
American politics has also been a significant endeavor to which many Arab Americans have made significant contributions. Within local, state, and federal levels, including members of Congress, governors, and mayors across the United States, Arab Americans stand with pride in holding and governing in many of these positions. Classic names such as Representative Ilhan Omar, Representative Rashida Tlaib, former Senator James Abourezk, Ralph Nader, Donna Shalala, and John Abizaid come to mind. Along with their active and past political roles, Arab Americans have constantly advocated for their rights and the rights of other minority groups during and after the civil rights movement. A figure such as James Abourezk was a profound politician regarding advocacy and civil rights.
One of the most significant fields of Arab American contribution can be seen within the broad field of science, including medicine, engineering, and physics. Arab American scientists in these various fields have made invaluable breakthroughs and advancements that have led to a healthier and more evolved American society.
In the earliest stages of Arab immigration, many Arabs were leaning their careers toward STEM, Medical, or law-based fields. Recently, Arab Americans and oncoming Arab immigrants have significantly contributed to the arts. Arab American writers, poets, and artists have produced works that reflect their experiences as immigrants or children of immigrants in America. Familiar names such as Helen Zhugaib and Heather Raffo come to mind when considering the Arab American experience through art and poetry. Arab American musicians have also significantly enriched American culture with their unique styles and sounds.
Conclusion:
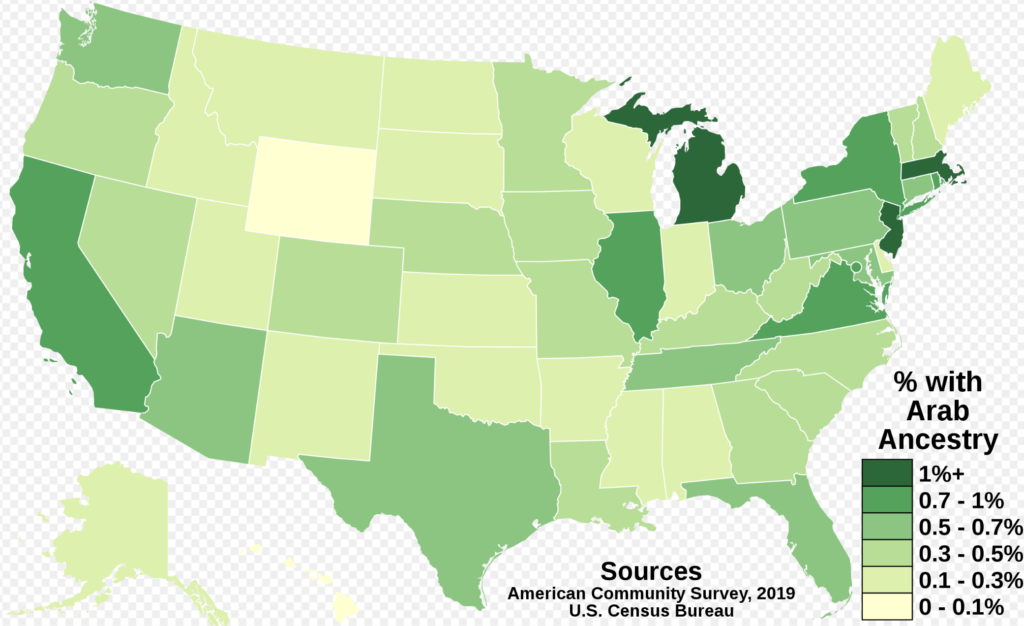
The History of Arab immigration to the United States has occurred throughout multiple phases, and its unique characteristics and challenges in each period are undeniable. Despite facing discrimination and challenges, Arab immigrants from the past and the present have made significant contributions to American society in various fields. Arab immigrants have generally had a very enriching impact on American culture and helped shape the country’s history and identity significantly.








